
The reaction mechanism of sulfuric acid with polyethylene, introducing
For instance, Lowry and Richardson say: "A reaction mechanism is a specification, by means of a sequence of elementary chemical steps, of the detailed process by which a chemical change occurs" [Lowry and Richardson, 1987, p. 190]. These two features of mechanisms are related and both are important to the role of mechanisms in understanding.

Reaction Mechanisms Overview ( Video ) Chemistry CK12 Foundation
We call each step in a reaction mechanism an elementary reaction. Elementary reactions occur exactly as they are written and cannot be broken down into simpler steps. Elementary reactions add up to the overall reaction, which, for the decomposition, is: 2O3(g) 3O2(g) (4.5.2) (4.5.2) 2 O 3 ( g) 3 O 2 ( g) Notice that the oxygen atom produced in.
Organic Chemistry Reaction Mechanism Pattern Examples YouTube
The reaction mechanism (or reaction path) provides details regarding the precise, step-by-step process by which a reaction occurs. The decomposition of ozone, for example, appears to follow a mechanism with two steps: O3(g) → O2(g)+O O+O3(g) → 2O2(g) O 3 ( g) → O 2 ( g) + O O + O 3 ( g) → 2 O 2 ( g)

The basic chemical reaction mechanisms of glycosylation. (a) Reaction
Enhance Your Shopping Experience With Our Personalised Recommendations. Choose From a Wide Selection Of Informative and Comprehensive Books For You.
Reaction Maps Now Available Master Organic Chemistry
Chem1 (Lower) 17: Chemical Kinetics and Dynamics 17.4: Reaction Mechanisms

Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions, Chemistry basics
The general rate law for a unimolecular elementary reaction (A → products) is. rate = k[A]. r a t e = k [ A]. For bimolecular reactions, the reaction rate depends on the number of collisions per unit time, which is proportional to the product of the concentrations of the reactants, as shown in Figur e 14.6.1 14.6. 1.

chemistry world E1 REACTION MECHANISM & EXAMPLES
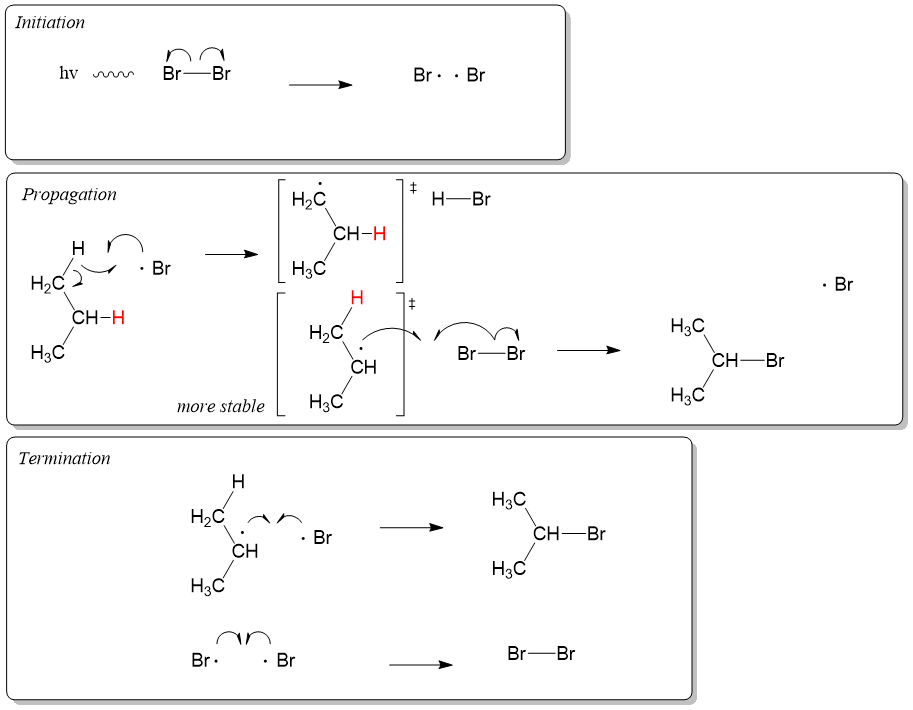
A reaction mechanism is the sequence of elementary steps by which a chemical reaction occurs. A reaction that occurs in two or more elementary steps is called a multistep or complex reaction. A reaction intermediate is a chemical species that is formed in one elementary step and consumed in a subsequent step.
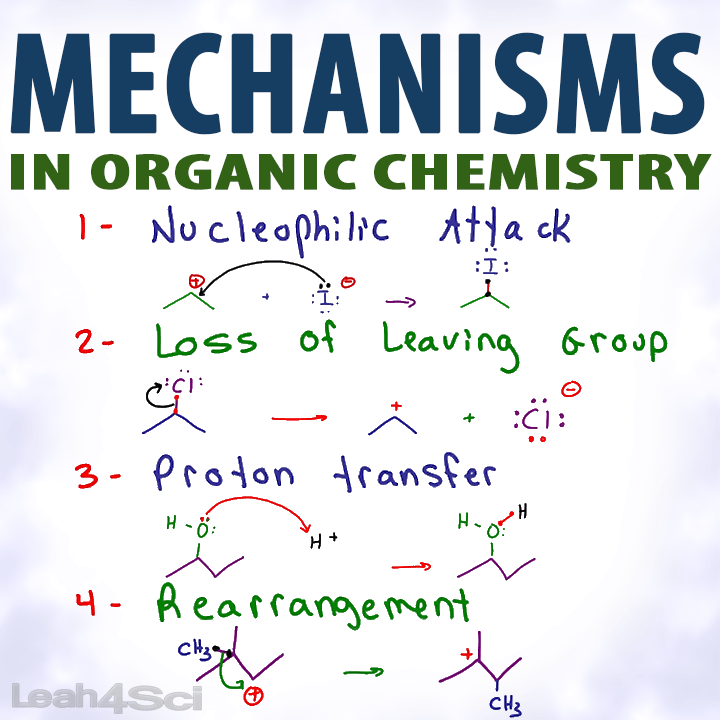
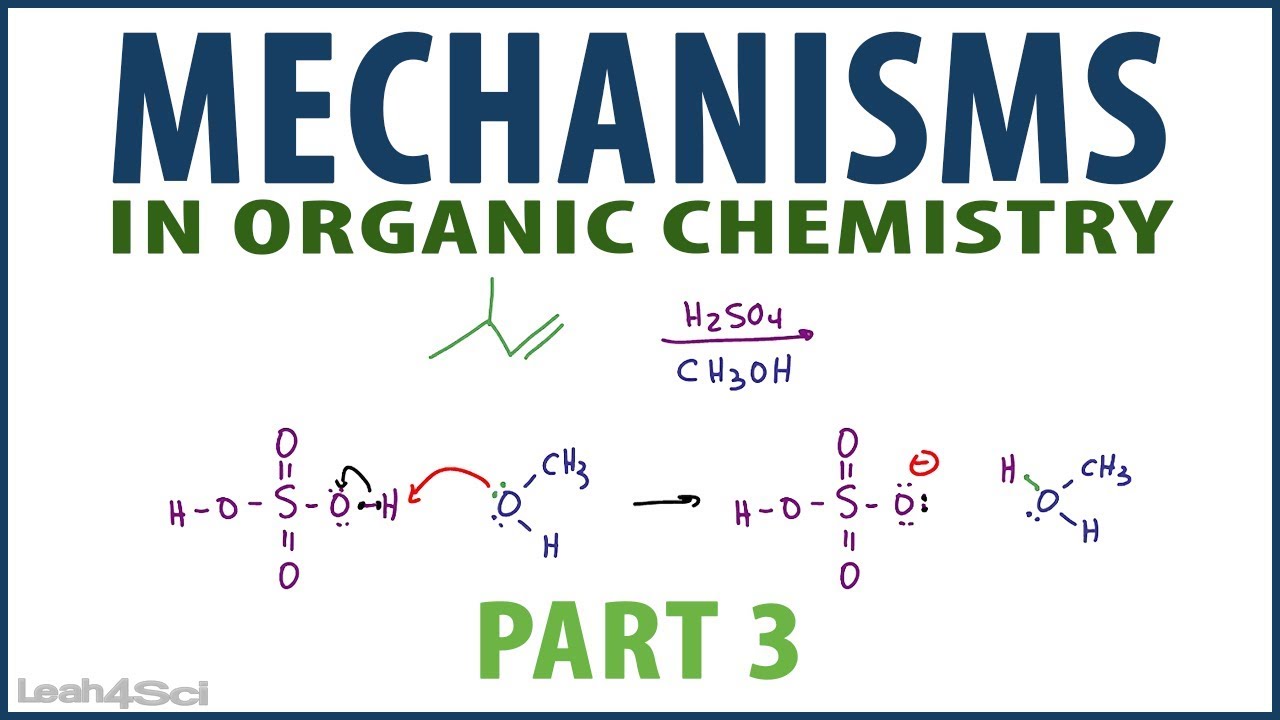
Organic Chemistry Mechanisms Tutorial Video Series by Leah4Sci
However, some unimolecular reactions may be the only step of a single-step reaction mechanism. (In other words, an "overall" reaction may also be an elementary reaction in some cases.) For example, the gas-phase decomposition of cyclobutane, C 4 H 8 , to ethylene, C 2 H 4 , is represented by the following chemical equation:
Organic Chemistry Mechanisms
A reaction mechanism is the sequence of elementary steps by which a chemical reaction occurs. Many reaction mechanisms contain one step that is much slower than the others; this step is known as the rate-determining step. If the rate-determining step is the first step in a mechanism, the rate law for the overall reaction can be derived directly.
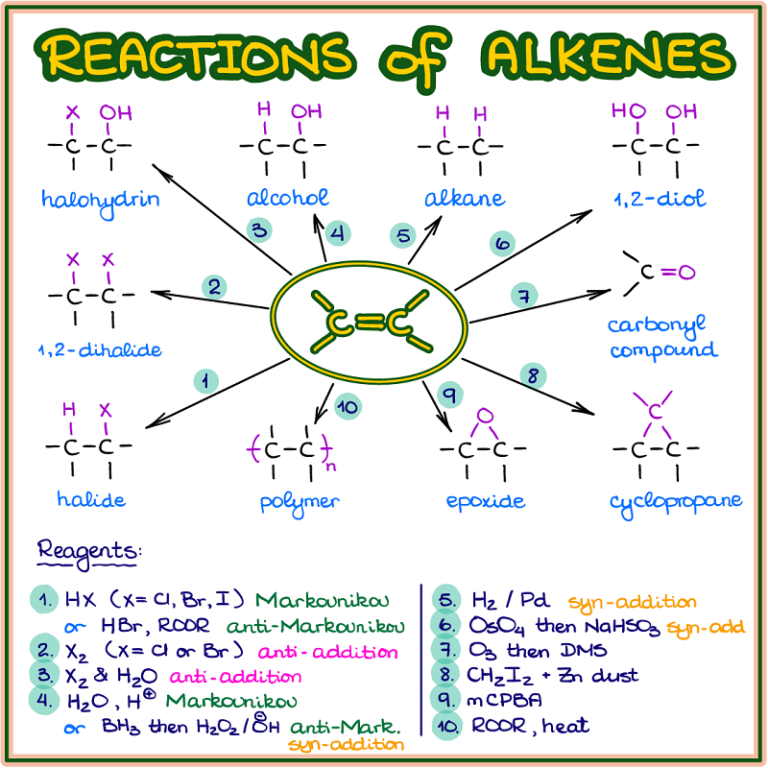
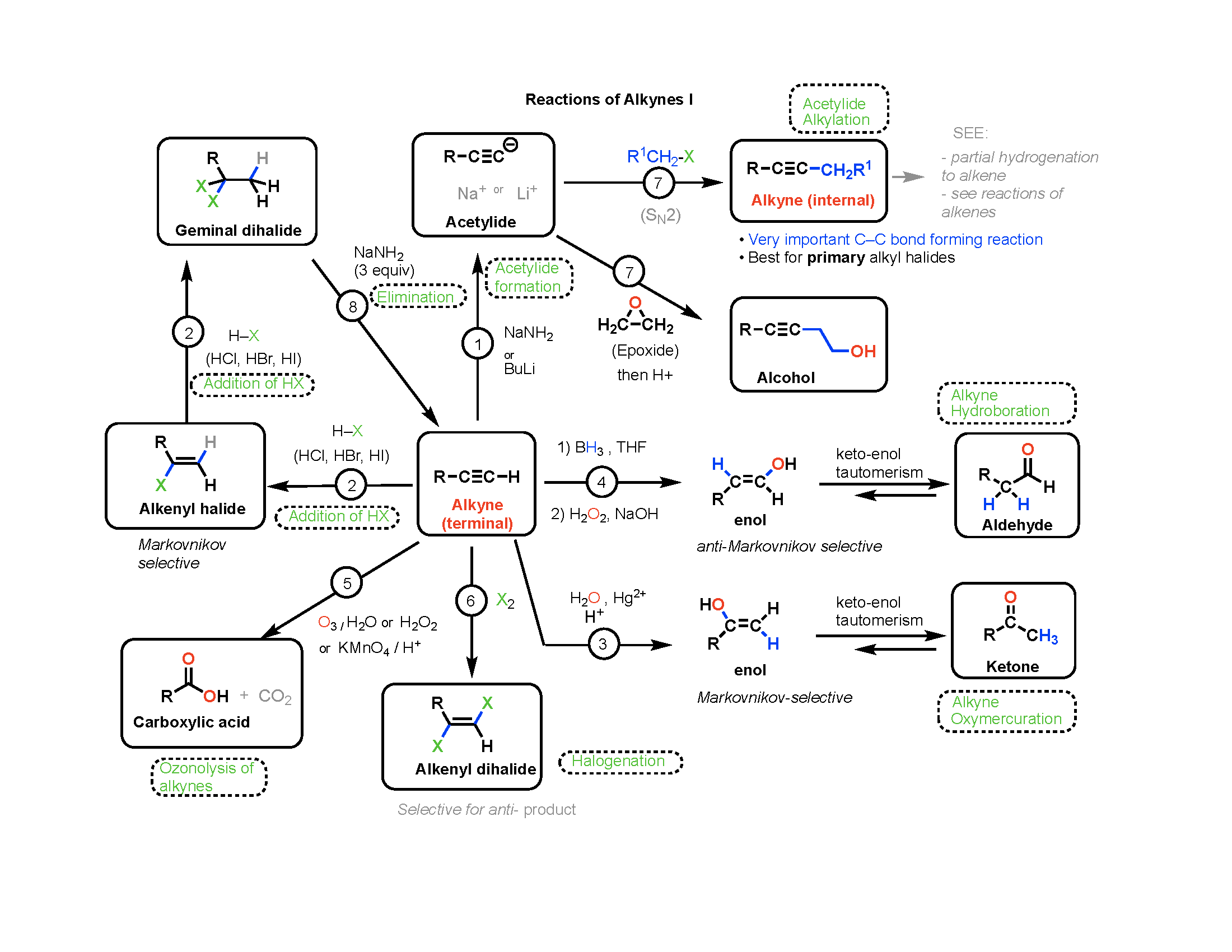
Reactions of Alkenes — Organic Chemistry Tutor
Article 20 December 2023 | Open Access Chemoselective umpolung of thiols to episulfoniums for cysteine bioconjugation Cysteine bioconjugation is an important method to modify biomolecules, but.

organic chemistry Mechanism of acidcatalyzed Robinson annulation
Chemical reactions, Kinetic analysis, Order, Reaction mechanisms, Students Abstract An introductory guide to deducing the mechanism of chemical reactions is presented. Following a typical workflow for probing reaction mechanism, the guide introduces a wide range of kinetic and mechanistic tools.
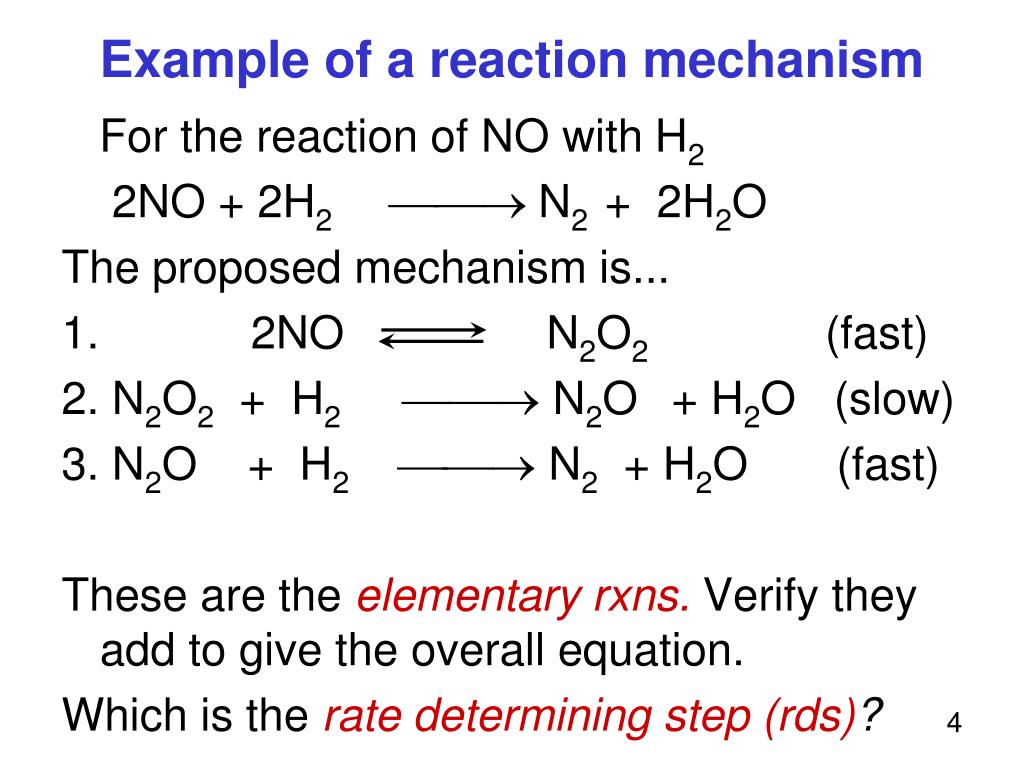
PPT Part V Reaction Mechanisms PowerPoint Presentation
The reaction mechanism (or reaction path) provides details regarding the precise, step-by-step process by which a reaction occurs. The decomposition of ozone, for example, appears to follow a mechanism with two steps: O3(g) O2(g) + O O +O3(g) 2O2(g) O 3 ( g) O 2 ( g) + O O + O 3 ( g) 2 O 2 ( g)
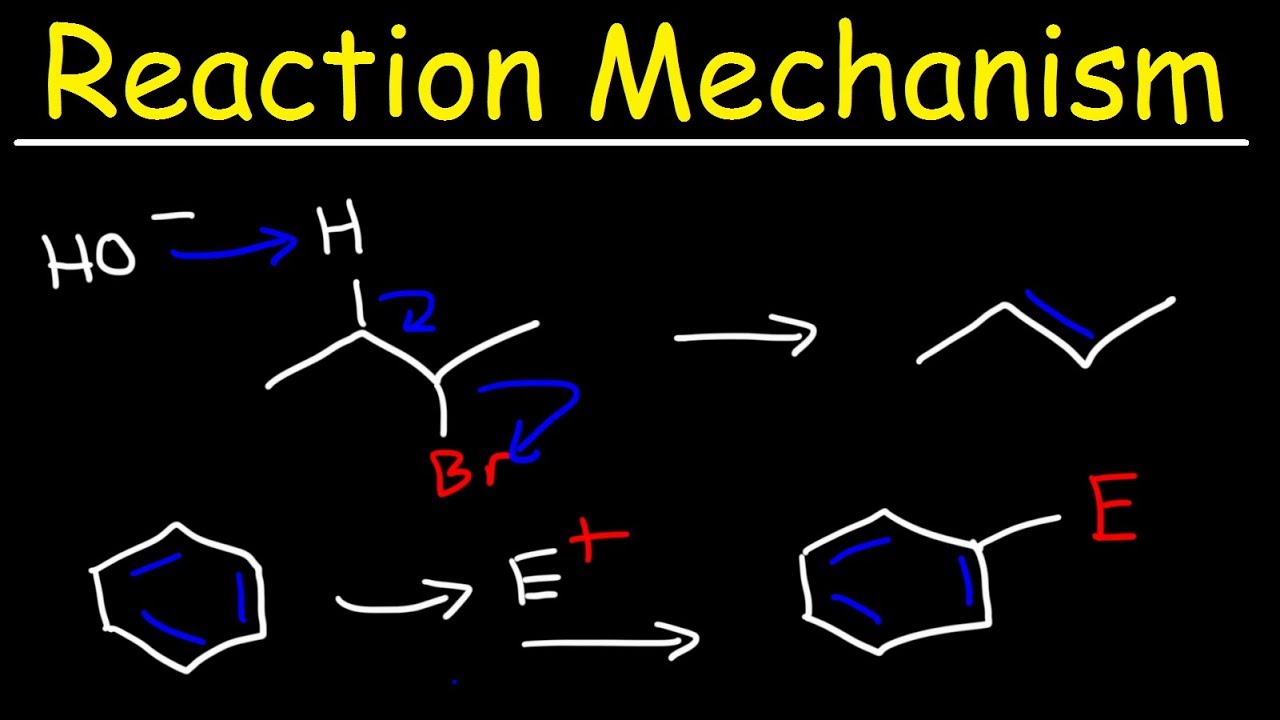
Organic Chemistry Reaction Mechanisms Addition, Elimination
reaction mechanism, in chemical reactions, the detailed processes by which chemical substances are transformed into other substances. The reactions themselves may involve the interactions of atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, and free radicals, and they may take place in gases, liquids, or solids —or at interfaces between any of these.
.png)
grinsend Überschreiten wie oft mechanism of chemical reaction Sozial
Reaction mechanisms | Organic Chemistry 1: An open textbook 7.5. Reaction mechanisms An acid-base (proton transfer) reaction For our first example of chemical reactivity, let's look at a very simple reaction that occurs between hydroxide ion and hydrochloric acid: HCl+OH− → H2O+Cl- (6.1.1) (6.1.1) H C l + O H − → H 2 O + C l -
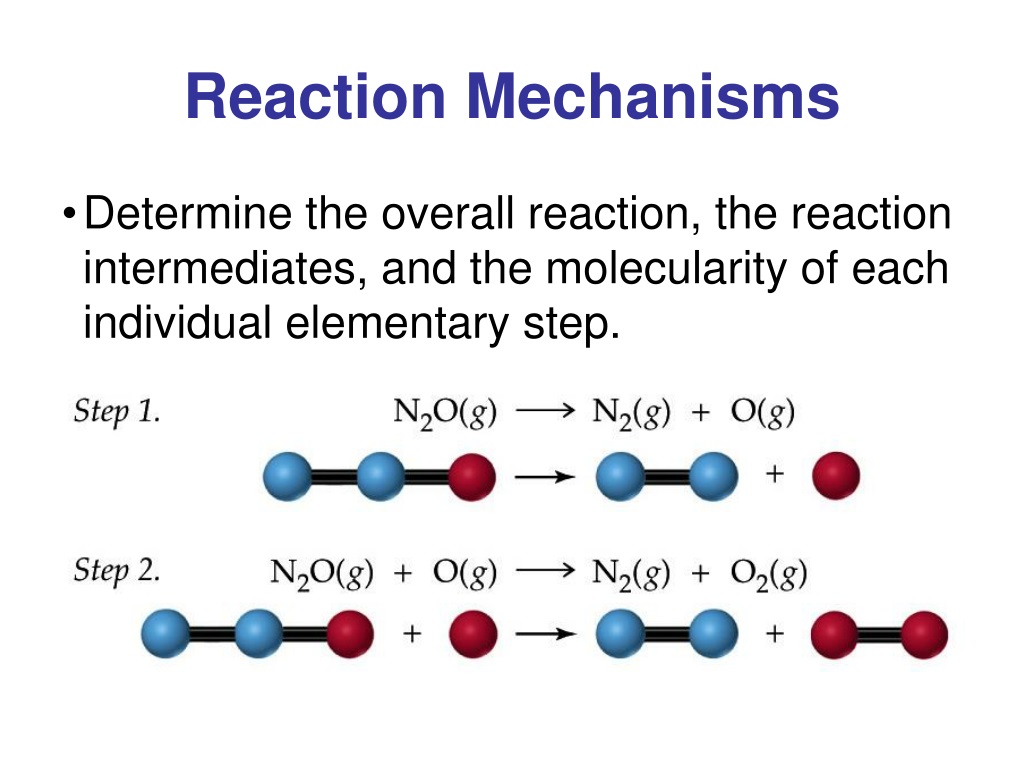
PPT Reaction Mechanisms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical reaction occurs. [1] A chemical mechanism is a theoretical conjecture that tries to describe in detail what takes place at each stage of an overall chemical reaction. The detailed steps of a reaction are not observable in most cases.
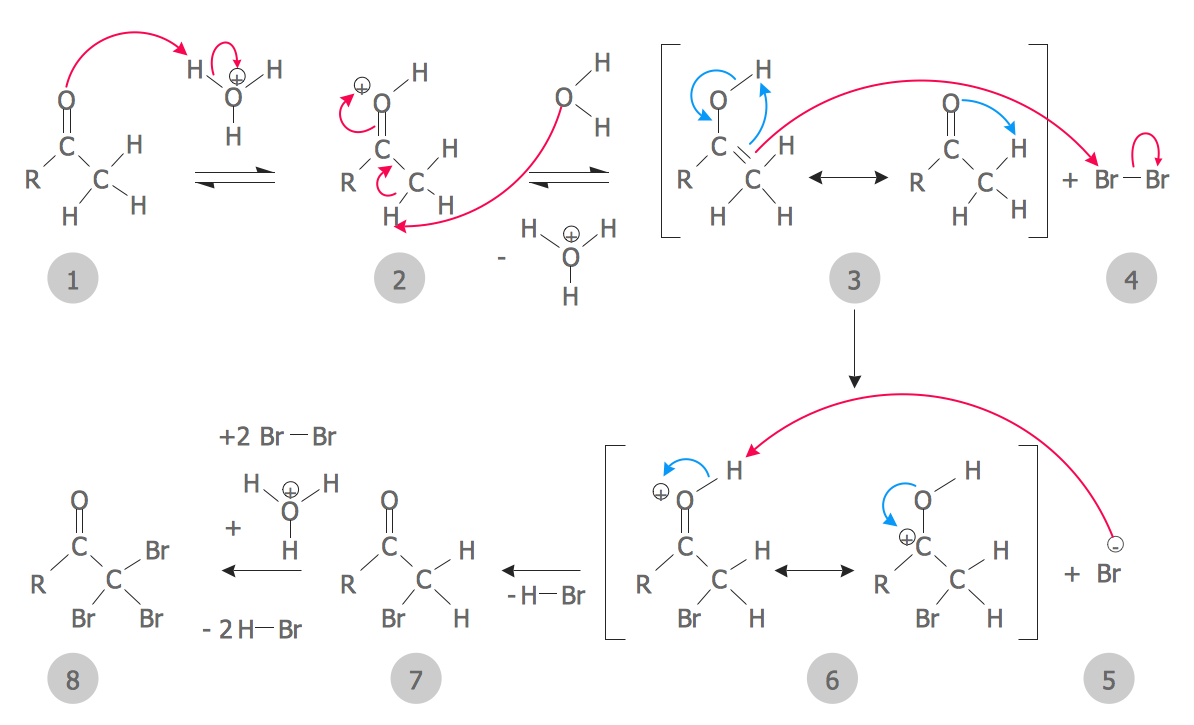
Chemistry Equation Symbols
Chemical reaction, a process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, the products. Substances are either chemical elements or compounds.. Chain reactions and photolysis reactions are examples of classification by reaction mechanism, which provides details on how atoms are shuffled.